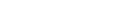원자력 발전소 안전성 향상을 위해서는 이와 관련된 해석코드의 수행이 필수적이다. 이러한 해석코드의 수행은 핵연료의 국부적인 부분에서 시작하여 피복재, 원자로 노심, 발전소 컴포넌트뿐 아니라 전체 계통에 대해서 이루어 진다. 이러한 연구를 수행하기 위해서 MATRA, FRAPCONE, MARS, PRISM, VISA, ANSYS 등 의 설계 해석코드들이 이용된다.
MATRA
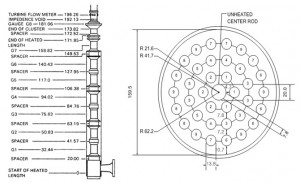
The reactor core including coolant, control and protection systems should be designed with appropriate margin to assure that SAFDL (Specified Acceptable Fuel Design Limits) are not exceeded during any condition of normal operation, including the effect of anticipated operational occurrences. The SFADL includes cladding overheating due to CHF or hydrodynamic flow instability and fuel melting. Therefore, the object of core thermal hydraulic design is to make sure coolability and fuel thermal integrity in the core during steady-state and anticipated operational occurrences. To do this, MATRA (Mutichannel Analyzer for steady-state and Transient in Rod Arrays) is studied for analyzing subchannel of the nuclear reactor. In PWR, CHF (Critical Heat Flux), fuel melting, and flow instability are the main thermal hydraulic design criteria. By using MATRA, the prediction of CHF is possible and other major parameters can be obtained.
FRAPCON
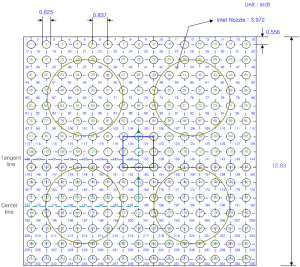
FRAPCON is one of the computational analysis code. It specially analyzes the fuel performance. The FRAPCON code had been developed to predict the behavior of fuel rods during long-term irradiation and to calculate initial conditions for transient analysis by combining features from “FRAP(Fuel Rod Analysis Program)” and “GAPCON(GAP CONductance)-THERMAL”. Recently updated FRAPCON code calculates the steady-state response of light water reactor fuel rods during long-term burnup.
The Scopes of FRAPCON are as follows:
- Heat conduction through the fuel and cladding
- Cladding elastic and plastic deformation,
- Fuel-cladding mechanical interaction
- Fission gas release
- Fuel rod internal gas pressure
- Heat transfer between fuel and cladding
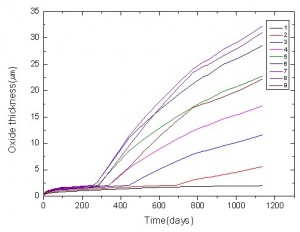
- Cladding oxidation
- Heat transfer from cladding to coolant
Simplified FRAPCON-3 Flow Chart
(Ref. NUREG/CR-6534 Vol. 2 PNNL-11513)
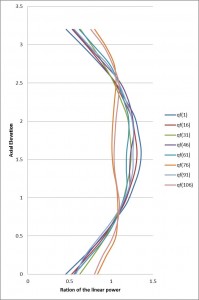
Power ratio at each step
MARS-LMR
MARS-LMR (Multi-dimensional Analysis Reactor System for Liquid Metal Reactor)
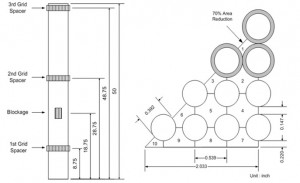
MARS-LMR is a safety analysis code for the safety function evaluation of system as SFR. This safety analysis code uses the coolants of future reactors such as sodium, lead-bismuth eutectic, helium, lithium, lithium-lead and so on. To analyze the future reactors, it has to generate the set of physical properties and thermodynamic tables of MARS code and those of Na, LBE are already generated by KAERI. Our lab also generated that of Gallium and is analyzing Ga-cooled PDHRS (Passive Decay Heat Removal System) is SFR.
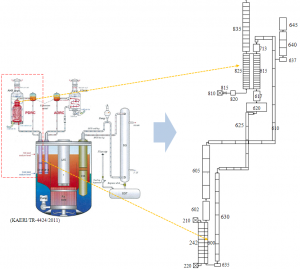
Nodalization of Ga-cooled PDHRS in KALIMER
VISA
ViSA is the Visual System Analyzer. ViSA is external environment program for MARS, RETRAN, RELAP5 and the programming language of ViSA is Delphi. The main features of ViSA are as follows:
- Online & post processing: X-Y trend graph vs. time
- Visualization of entire system behavior: System mimic with several gauges & Nodalization map for volume properties (boron, void, liquid/gas temperature,..)
- Interactive control : Simplifying control input for complex manual operation in EOP
- Miscellaneous functions : Control / Geometric input editor for modification & Replay (similar to strip function in MARS), 3-D power visualization (MASTER DLL required), Engineering unit conversion
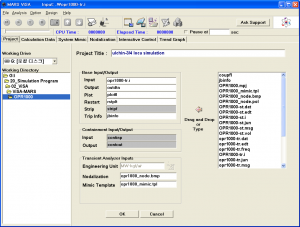
Project tab of ViSA (OPR-1000)
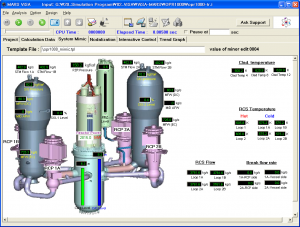
System mimic tab of ViSA (OPR-1000)
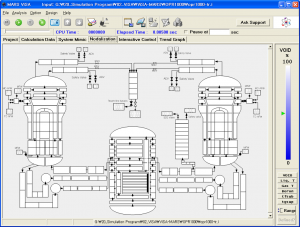
Nodalization tab of ViSA (OPR-1000)
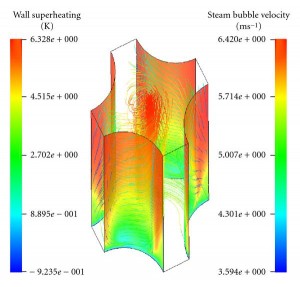
CFD
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with surfaces defined by boundary conditions. With high-speed supercomputers, better solutions can be achieved. Ongoing research yields software that improves the accuracy and speed of complex simulation scenarios such as transonic or turbulent flows.
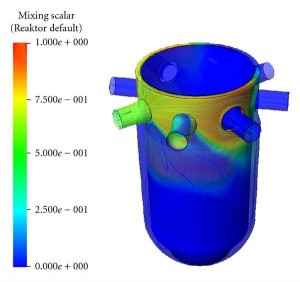
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is increasingly being used in nuclear reactor safety analyses as a tool that enables safety relevant phenomena occurring in the reactor coolant system to be described in more detail. Numerical investigations on single phase coolant mixing in Pressurized Water Reactors (PWR) have been performed. The work is aimed at describing the mixing phenomena relevant for both safety analysis, particularly in steam line break and boron dilution scenarios, and mixing phenomena of interest for economical operation and the structural integrity.